Carbon offsetting is helping Rwanda reduce transportation emissions, which account for 13% of its greenhouse gases in 2025. Here’s the key info:
- Goal: Achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 through e-mobility and renewable energy projects.
- Key Initiatives:
- Electric Buses: Converting 20% of Kigali’s bus fleet to electric by 2030 could cut 72,000 tCO2eq emissions.
- Electric Motorcycles: Ampersand‘s program saves $22M annually on fuel imports.
- Incentives: Zero VAT on EV imports, tax breaks, and support for EV infrastructure.
- Partners: GGGI, UNEP, World Bank, and private companies like Ampersand and AutoMag.RW.
Rwanda Electric Vehicles
Carbon Offsetting in Rwanda’s Transportation
Transportation Emissions in Rwanda
Road transport is responsible for 13% of Rwanda’s greenhouse gas emissions, and this number is expected to increase due to growing vehicle use and population [1][2]. To address this, Rwanda has introduced the Green Growth and Climate Resilience Strategy (GGCRS). This plan prioritizes better engine efficiency, adoption of modern technologies, infrastructure upgrades, and more efficient transportation systems [1][2]. A key part of this strategy is the focus on e-mobility to reduce emissions and build a more sustainable transport sector.
Electric Vehicles and Emission Reduction
Rwanda’s push for e-mobility highlights its dedication to cutting transportation-related emissions. The government has introduced several incentives to encourage the use of electric vehicles (EVs). These include zero VAT on EV imports, lower charging costs, tax breaks for businesses in the EV sector, and land allocations for charging stations. Additionally, there’s support for local EV production [2][3]. Companies like VW Mobility Solutions, Victoria Autofast Rwanda, Ampersand, Rwanda Electric Motorcycle Ltd, and Safi/Gura Ride have already invested in Rwanda’s e-mobility sector [2][3]. AutoMag.RW is another key player, actively supporting the adoption of EVs across the country.
AutoMag.RW and Sustainable Transportation
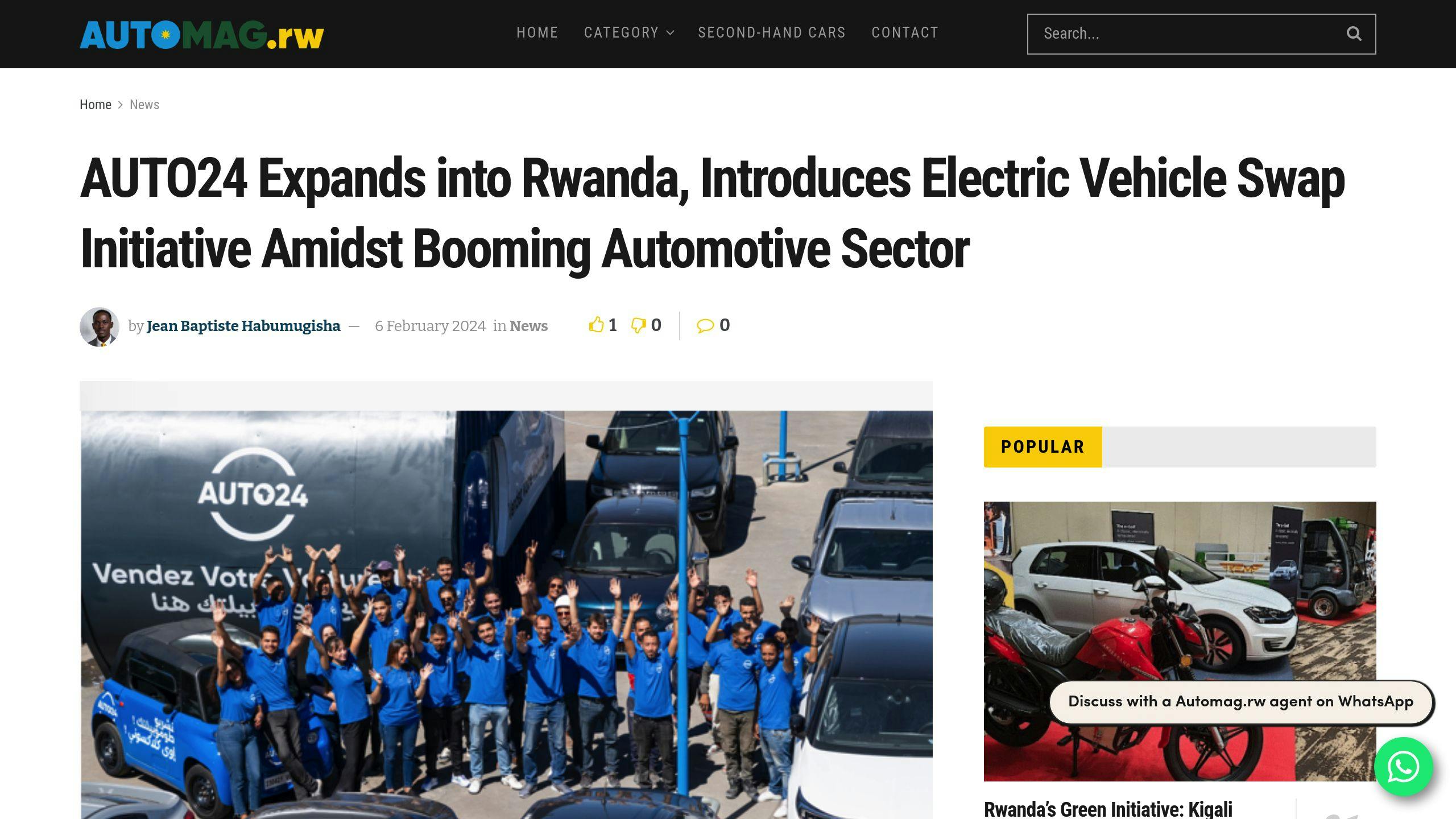
AutoMag.RW plays an important role in advancing Rwanda’s e-mobility goals by improving access to EVs and promoting awareness about environmentally friendly transportation. Working closely with government programs and organizations like the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI), UNEP, and the World Bank, AutoMag.RW contributes to the development of EV infrastructure and sustainable transport solutions [2][3]. This collaboration supports Rwanda’s vision for a more efficient and resilient transportation system.
sbb-itb-7bc66b5
How Carbon Offsetting Works in Rwanda
Carbon Offsetting Projects
Rwanda has been focusing its carbon offset efforts on three key areas: renewable energy, reforestation, and sustainable transportation. These projects aim to cut greenhouse gas emissions while supporting the country’s broader environmental goals.
One standout initiative is Kigali’s electric bus program, backed by the Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI). This project plans to convert 20% of the city’s bus fleet to electric vehicles by 2030, aiming to cut 72,000 tCO2eq emissions [2]. Another example is Ampersand’s electric motorbike program, supported by partners like the Shell Foundation, which highlights the private sector’s role in these efforts.
| Project Type | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Electric Buses | 72,000 tCO2eq emissions cut by 2030 |
| Electric Motorcycles | Rwf 23 billion saved annually on fuel |
| Renewable Energy | Builds infrastructure for EV charging |
These projects are making measurable progress in reducing emissions. However, their success depends on robust certification and verification processes to ensure transparency and accountability. Together, these initiatives are central to Rwanda’s plan to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
Certification and Verification
To maintain the integrity of its carbon offset projects, Rwanda requires strict adherence to international standards. Each project must prove:
- Additionality: The emission reductions wouldn’t happen without the project.
- Permanence: The benefits must last over the long term.
- Verifiability: Third-party audits must confirm the results.
These certifications involve detailed audits by recognized bodies to confirm compliance. To further encourage adoption, the Rwandan government provides financial incentives and supportive policies, ensuring these projects remain effective and credible in the fight against climate change.
Participating in Carbon Offsetting Programs
Calculating Your Carbon Footprint
REMA offers tools to help measure transportation emissions by tracking factors like vehicle type, fuel consumption, and travel distance. Businesses can also use specialized calculators to assess emissions from their fleets. After calculating your emissions, the next step is to choose the right offset projects to support.
Choosing Offsetting Projects
When exploring carbon offset projects in Rwanda, look for initiatives certified by VCS or Gold Standard to ensure credibility. Examples include e-mobility programs that cut emissions while lowering fuel costs, and public transport projects that enhance urban mobility. Infrastructure projects, approved by REMA, also contribute to long-term goals.
Ampersand’s program is a great example of how certified projects align with Rwanda’s offsetting objectives, showing how businesses can integrate their goals with the country’s sustainability targets [4].
Challenges and Opportunities
Shifting to carbon offsetting comes with hurdles but also presents opportunities for businesses in Rwanda. For example, transitioning to e-mobility requires a hefty investment of around US $900 million [1][2]. To ease this burden, the government offers incentives like tax breaks, low-interest loans, and land for charging stations.
The International Carbon Reduction and Offset Alliance (ICROA) provides guidelines for purchasing carbon credits, making it easier for businesses of all sizes to participate. Partnerships such as GGGI’s electric bus program in Kigali highlight how organizations can work with the government to meet national emission reduction goals [5].
These combined efforts are helping Rwanda take a leading role in sustainable transportation and carbon offsetting.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Rwanda’s carbon offsetting efforts in the transportation sector highlight its dedication to reducing emissions and promoting sustainable mobility. A key goal is to electrify 20% of buses by 2030, which is expected to cut emissions by 72,000 tCO2eq [2].
Private sector investments in e-mobility, along with public-private collaborations, are speeding up Rwanda’s shift to cleaner transport. By linking carbon offsetting with e-mobility and renewable energy initiatives, the country is taking a well-rounded approach to meet its carbon neutrality goals.
Switching to electric vehicles not only lowers emissions but also decreases reliance on expensive fuel imports, providing long-term economic advantages. The government’s mix of fiscal incentives and infrastructure development has created a favorable environment for carbon offsetting projects.
Kigali’s electric bus program stands out as a clear example of how Rwanda is using its renewable energy resources to improve public transportation.
"The electric buses in Kigali aim to fulfill increasing demand on the current public transport system and take full advantage of the Rwandan grid, which is supplied predominantly by hydropower" [5].
The success of these programs relies on continued collaboration between the public and private sectors, including investments in EV infrastructure and international support for renewable energy projects. Through certified offset projects, forward-thinking e-mobility solutions, and strategic partnerships, Rwanda is not only cutting emissions but also creating economic opportunities and improving urban mobility for its people.
Related posts
- Rwanda EV Import Duty Exemptions Explained
- EVs vs. ICE Cars: Performance on Rwanda’s Roads
- 5 Common Car Shipping Issues to Rwanda
- New vs. Used Cars: Cost Breakdown in Rwanda





