Reducing fleet emissions in Rwanda is critical as road transport contributes 13% of the country’s total greenhouse gas emissions and 57% of emissions within the energy sector. With vehicle registrations increasing by over 61,000 between 2021 and 2023, emissions are rising alongside public health risks caused by pollutants from older diesel engines. Here’s how you can address this issue:
- Audit Fleet Emissions: Use tools like the Kigali Carbon Accounting Tool (KCAT) and conduct mandatory emissions testing.
- Replace High-Emission Vehicles: Focus on older models and transition to electric vehicles (EVs), which are exempt from emissions testing and offer tax advantages.
- Optimize Routes: Minimize travel distances using GPS and route planning software to cut fuel use and emissions.
- Adopt Electric Vehicles: EVs reduce lifetime emissions by 50%, save fuel costs, and benefit from VAT and duty exemptions in Rwanda.
- Upgrade to Electric Buses and Motorcycles: Electric buses and e-motorcycles lower operating costs and emissions, with government incentives making them more accessible.
- Install Smart Charging Infrastructure: Set up workplace charging stations, use off-peak tariffs, and integrate solar power to manage grid demand.
Switching to EVs and optimizing fleet operations align with Rwanda’s goal of having 70% of new vehicle registrations electric by 2035. AUTO24.rw simplifies EV adoption by offering a variety of certified electric vehicles and trade-in options. By acting now, businesses can cut costs, comply with regulations, and contribute to cleaner air in Rwanda.
Understanding Rwanda’s journey to e-mobility
Assess Current Fleet Emissions
Understanding your fleet’s baseline emissions is the first step in identifying the vehicles that contribute the most to your carbon footprint.
Take advantage of Rwanda’s specialized tools like the Kigali Carbon Accounting Tool (KCAT), official carbon footprint templates from the Rwanda Climate Change Portal, and the Rwanda GHG Activity Data Platform. These resources are designed to help you accurately measure and report your fleet’s emissions. They provide a solid foundation for conducting a thorough emissions audit.
Conduct an Emissions Audit
To start, calculate emissions for every vehicle in your fleet. The GHG Protocol’s "GHG Emissions from Transport or Mobile Sources" worksheet offers a structured framework for creating an inventory of emissions from mobile sources. This step-by-step audit will help you understand each vehicle’s impact and prepare for official inspections.
In Rwanda, all vehicles – except fully electric ones – are required to undergo mandatory emissions testing at authorized Contrôle Technique centers located in Remera, Rwamagana, Huye, and Musanze. For commercial vehicles, inspections must be done twice a year, while private vehicles require testing once annually. You can schedule these inspections through the IremboGov platform, which also allows you to download digital emission certificates. These certificates indicate whether a vehicle has passed or failed.
Here’s a breakdown of the official inspection fees:
| Vehicle Category | Inspection Fee (RWF) |
|---|---|
| Passenger transport (up to 8 seats) | 34,940 |
| Passenger transport (9 seats or more) | 51,578 |
| Goods transport (over 1.5 tons) | 51,578 |
| Other motor vehicles | 49,914 |
Before booking an inspection, make sure to clear any outstanding traffic fines, as this is a requirement. If a vehicle fails inspection, you can take advantage of a 50% discount on re-testing fees, provided the re-inspection is completed within 14 days. To save time, consider scheduling emission and mechanical inspections together to avoid multiple trips.
Identify High-Emission Vehicles
Once the audit is complete, use the data to focus on the vehicles that are the biggest polluters. Emission certificates from Contrôle Technique centers will clearly identify vehicles exceeding pollution limits. Cross-check these results with your GHG Protocol calculations to pinpoint high-emission vehicles, which are often older models with internal combustion engines.
Prioritize replacing vehicles that consistently fail inspections or exhibit high emissions. Fully electric vehicles, which are exempt from mandatory emission testing in Rwanda, offer a long-term solution for reducing fleet emissions. For commercial fleets, the bi-annual inspection schedule provides regular opportunities to catch and address engine performance issues early.
This assessment does more than ensure compliance – it helps guide strategic decisions for fleet upgrades and transitions. With Kigali’s peak power demand expected to grow by 64% by 2030, understanding your fleet’s emissions today can help you plan for a sustainable future. Using smart charging strategies based on fleet usage data can also ease the load on power distribution networks by as much as 15%.
Implement Route Optimization
To tackle emissions from high-pollution vehicles, refining routes is a must. Route optimization slashes fuel use and greenhouse gas emissions by cutting down travel distances and time on the road. Rwanda’s Green Growth and Climate Resilience Strategy (GGCRS) highlights the importance of creating "efficient operational systems" to reduce emissions per kilometer traveled. In Kigali, businesses must also factor in local policies like car-free zones and car-free days, which are part of the city’s broader push toward decarbonization. François Zirikana, an E-mobility Specialist for the City of Kigali, emphasizes:
"E-mobility is one of the transport decarbonization initiatives the government has undertaken. Other initiatives include Kigali bike share scheme as well as car-free zones and car-free days".
Leveraging precise GPS tools and route planning software can turn route optimization into tangible fuel and energy savings.
Use GPS and Route Planning Tools
GPS and route planning software are invaluable for finding the shortest, fastest paths for vehicles. This reduces time spent on the road, lowers fuel costs, and cuts emissions. For electric vehicle (EV) fleets, specialized tools like A Better Routeplanner can calculate optimal charging stops based on the vehicle model and real-time battery data. These tools help plan trips that include charging station locations and estimate the vehicle’s arrival State of Charge (SoC). This is particularly useful in Kigali, where nearly 200 EV charging stations are available downtown.
Rwanda’s hilly landscape adds another layer of complexity to route planning. Optimized routes should reduce strain on vehicle transmission and braking systems, improving both fuel and energy efficiency. Driver training can also make a difference – teaching techniques for managing braking on steep roads helps prevent engine overheating and energy waste. Additionally, aligning routes with charging infrastructure ensures EV fleets stay operational without unnecessary downtime. Smart charging strategies, such as charging during off-peak hours or syncing with solar power generation, further boost efficiency and stabilize the grid.
Reduce Idle Time
Optimized routes are just the beginning; cutting idle time is another way to reduce fuel waste and emissions. Internal combustion vehicles burn fuel and release pollutants with every minute of idling, while electric vehicles completely eliminate emissions during idle time.
Smart charging plays a critical role in minimizing idle time for electric fleets. By using cost-reflective electricity pricing, vehicles can be charged during off-peak hours, ensuring they are fully charged and ready to go without delays. Tarek Keskes, a World Bank ESMAP Energy Specialist, underscores this point:
"Our analysis shows that Rwanda can achieve its goals if smart charging, cost-reflective tariffs, and integrated planning are prioritized".
Strategically placing charging infrastructure at key transit hubs like the Nyabugogo Terminal, supported by rooftop solar panels and battery storage, further reduces downtime and eliminates unnecessary trips for refueling.
Adopt Electric Vehicles via AUTO24.rw
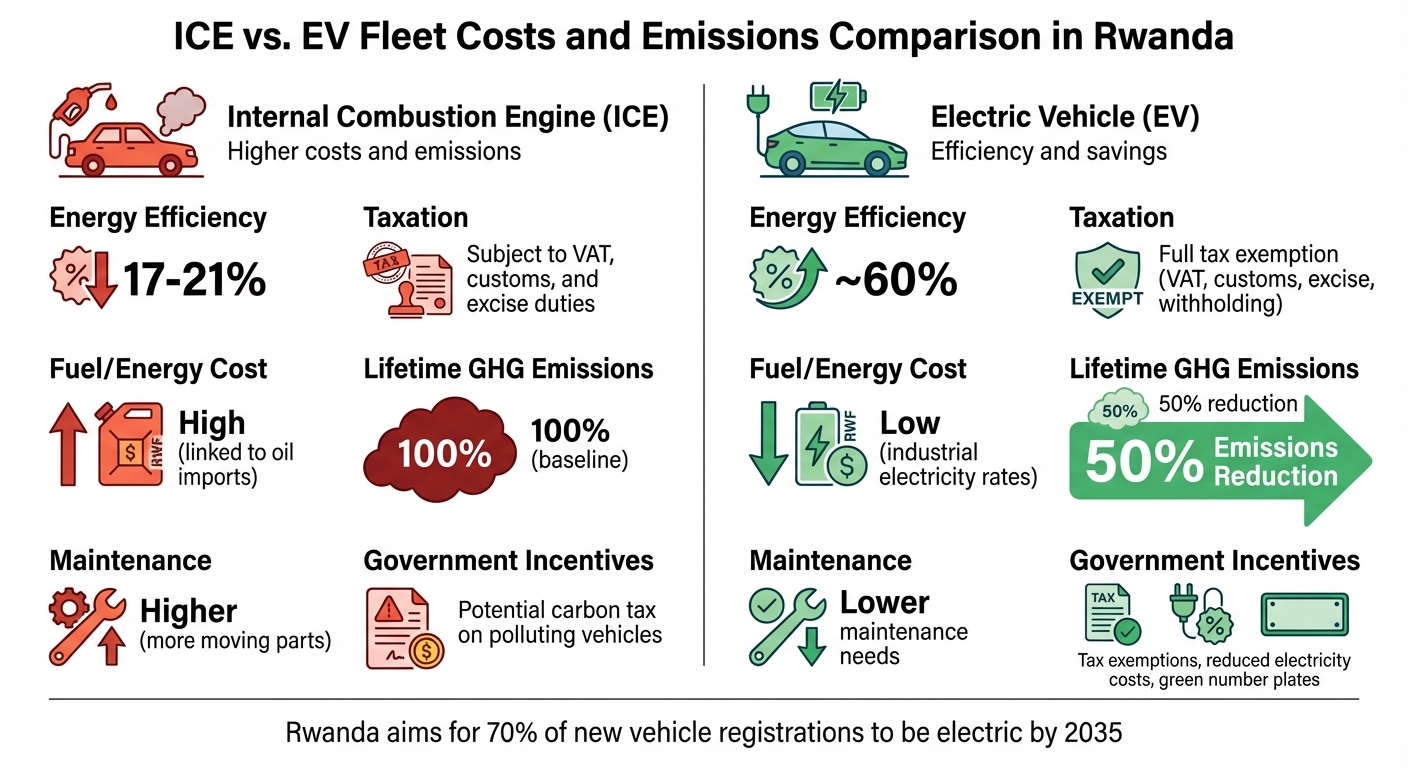
ICE vs Electric Vehicle Fleet Costs and Emissions in Rwanda
Switching from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs) offers a powerful way to reduce fleet emissions in Rwanda while aligning with the country’s ambition to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. EVs are not only more energy-efficient – boasting around 60% efficiency compared to the 17%–21% of ICE vehicles – but they also come with significant tax advantages. These include exemptions from VAT, customs duties, excise duties, and withholding taxes. Additionally, EV users enjoy access to Rwanda’s lowest industrial electricity rates. Williams Buningwire, Acting Spokesperson for the Rwanda Private Sector Federation (PSF), highlights the broader benefits of this transition:
"The transition to green mobility is a national effort. There are multiple benefits of electric vehicles compared to diesel-powered vehicles. They reduce air pollution and help save the money previously spent on fuel imports."
Take electric motorcycles as an example: transitioning to these alone could save Rwanda’s economy $22 million annually in fuel imports. Beyond reducing emissions, EVs offer an opportunity for significant cost savings.
Benefits of EV Adoption
The advantages of adopting EVs go beyond cutting costs. Replacing a traditional gas-powered car with an electric one can slash greenhouse gas emissions by half over the vehicle’s lifetime. This is a critical step for improving air quality, especially in urban centers like Kigali, where traffic-related pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) are linked to serious health issues, including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. EVs also contribute to quieter streets – an often-overlooked benefit in densely populated areas.
Government policies make the switch even more appealing. Businesses in the e-mobility sector are eligible for a reduced corporate income tax rate of 15%. EVs are also issued green number plates, which come with perks like priority parking and potential free access to certain high-traffic zones. These incentives lower the initial hurdles for adopting EVs, making the transition more attractive for businesses and individuals alike.
ICE vs. EV Fleet Costs and Emissions Comparison
A direct comparison highlights why EVs are a smarter choice for both finances and the environment:
| Feature | Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) | Electric Vehicle (EV) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | 17%–21% | Approximately 60% |
| Taxation (Rwanda) | Subject to VAT, customs, and excise duties | Full tax exemption (VAT, customs, excise, withholding) |
| Fuel/Energy Cost | High (linked to oil imports) | Low (industrial electricity rates) |
| Lifetime GHG Emissions | Baseline (100%) | Reduced by about 50% |
| Maintenance | Higher (more moving parts) | Lower maintenance needs |
| Government Incentives | Potential carbon tax on polluting vehicles | Tax exemptions, reduced electricity costs, and green number plates |
Rwanda’s regulatory landscape is evolving to favor EVs. For instance, a five-year age limit on imported second-hand ICE cars has been implemented, and a carbon tax on polluting vehicles is under consideration. These measures make ICE fleets increasingly expensive to maintain, while EV incentives are guaranteed through at least June 2028.
How AUTO24.rw Supports EV Adoption
AUTO24.rw simplifies the transition to electric fleets by offering a wide selection of EVs tailored to various needs, including high-performance brands like Tesla, Leapmotor, and ROX. Whether your business requires light-duty delivery vehicles or heavy-duty transport options, AUTO24.rw has you covered. Their team of experts is available via WhatsApp to provide personalized advice, from choosing the right vehicle to understanding maintenance and charging infrastructure.
To ease the upfront costs, AUTO24.rw also offers trade-in options, allowing businesses to sell their current ICE vehicles and reinvest in EVs. They provide detailed technical documents and expert guidance to help fleet managers navigate EV specifications and operational requirements.
With Rwanda aiming for 70% of all new vehicle registrations to be electric by 2035, AUTO24.rw equips businesses to stay ahead of these changes while reaping the financial and environmental rewards of going electric.
sbb-itb-7bc66b5
Deploy Smart Charging Infrastructure
After optimizing routes and embracing EV adoption, the next critical step is building a reliable charging infrastructure. Efficient charging systems are key to keeping your fleet running smoothly. However, Rwanda’s electricity grid is already stretched thin, with some lines in Kigali operating at 136% capacity. This reality calls for a strategic approach to vehicle charging.
Install Workplace Charging Stations
Setting up charging stations at your business location involves working with MININFRA, RURA, and REG. The first step is evaluating your facility’s grid capacity, particularly in urban areas.
When selecting chargers, opt for devices that support CCS2 and GB/T standards. This ensures compatibility with a variety of vehicle types and keeps your fleet adaptable as it grows. The power rating of chargers also plays a significant role in grid impact. Research shows that 10 kW chargers caused only two out of 18 transformers to exceed 80% loading, while 20 kW chargers pushed seven transformers past that threshold.
| Charger Type | Impact on Transformer Loading (>80% capacity) | Recommended Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 10 kW Charger | 2 out of 18 transformers exceeded 80% loading | Ideal for standard overnight charging |
| 20 kW Charger | 7 out of 18 transformers exceeded 80% loading | Requires grid upgrades or backup power |
To ease grid pressure, consider pairing your charging stations with rooftop solar panels and battery storage. A great example is the Nyabugogo multi-modal transit hub in Kigali, which features 18 chargers powered by an 800-kW solar photovoltaic system and battery storage. This setup reduces reliance on the grid and lowers operational costs over time. While the project cost $7.7 million, it demonstrates how self-sustaining systems can be both effective and efficient. Across Rwanda, MININFRA has identified over 226 potential sites for charging stations, focusing on busy areas with high traffic.
Government incentives can help offset installation costs. For example, import duties on EV accessories, including charging equipment, are waived, and special lower electricity tariffs for EV charging are available. These benefits make it easier to manage upfront costs and shorten the time needed to see a return on your investment.
By combining these measures, businesses can create smarter charging setups that save money and reduce strain on the grid.
Use Off-Peak Charging Tariffs
Timing is everything when it comes to charging. Rwanda is moving toward time-of-use (ToU) tariffs, which reward businesses for charging during off-peak hours when the grid is under less demand. Currently, EV charging is often billed at industrial rates, but the government is introducing more cost-effective pricing models to encourage e-mobility.
Smart charging systems can schedule charging for these off-peak hours, lowering costs and easing grid pressure. Tarek Keskes, an Energy Specialist at the World Bank, highlights the benefits:
"Smart charging offers one of the most effective tools to ease pressure on the grid. Shifting charging to off-peak hours and aligning it with solar generation can reduce stress on distribution networks by up to 15%."
This isn’t just a cost-saving tactic – it’s a way to improve grid stability. Kigali’s peak power demand is expected to surge 64% by 2030, even without considering the added load from EVs. Without better charging management, overloaded power lines could quadruple by then. Charging during off-peak times helps prevent this while also cutting your electricity bills.
Installing smart charging software can automate these schedules, ensuring your vehicles are fully charged and ready for the day. Some advanced systems even support Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, which allows fleet batteries to send power back to the grid during peak hours, potentially generating extra income.
Stay updated on tariff announcements from RURA. Adapting your charging strategy to evolving pricing models can help you secure the lowest rates. With the government’s focus on promoting e-mobility, more favorable pricing structures are expected, making early investment even more appealing.
Transition to Electric Buses and E-Motos
Electric buses and motorcycles are shaping up to be game-changers for public transport and delivery businesses. They not only slash emissions but also help cut operating costs. In Rwanda, these vehicles are a natural fit for urban areas, where shorter travel distances and strong government backing make the transition more viable than ever. Let’s take a closer look at how electric buses and e-motos are driving efficiency in these sectors.
Advantages of Electric Buses
Electric buses bring a double benefit: they reduce both costs and emissions. Considering that buses account for about 39.1% of greenhouse gas emissions in Rwanda’s transport sector, the shift to electric models holds significant potential for environmental improvement.
The financial case for electric buses is also compelling. Current incentives, like VAT exemptions, duty waivers on EV components, and reduced electricity tariffs, make these buses cost-competitive with diesel models in just three years. Yizere Ange from GGGI Rwanda highlights this progress:
"The current incentives have reduced the cost parity between electric and diesel buses by a full three years, meaning the operators will have the same TCO for electric buses as diesel buses after only three years of operation".
The government is doubling down on this transition. By September 2025, all new buses introduced to Kigali will be electric, a commitment led by the Ministry of Infrastructure under Dr. Jimmy Gasore. This initiative is supported by state-owned Ecofleet Solutions and the World Bank’s Rwanda Urban Mobility Improvement Project (RUMI). Private companies like BasiGo and IZI are also piloting electric bus models, showcasing the practicality of this shift. By 2030, Rwanda aims to have 20% of its bus fleet running on electric power.
Adopt E-Motos for Deliveries
Electric motorcycles, or e-motos, are another practical step toward a cleaner fleet, especially for delivery services. Operating a petrol motorcycle costs about $2,000 annually, but switching to an e-moto cuts that by roughly a third, saving riders around $700 each year. This translates to a 35% boost in weekly earnings for e-moto riders compared to those using petrol bikes.
Ampersand, a Kigali-based startup, is leading the charge in this space. By May 2024, the company had deployed over 2,200 e-motorcycles and set up 26 charging stations across Rwanda. Their battery-swapping model allows riders to exchange a depleted battery for a fully charged one in under five minutes, ensuring minimal downtime for delivery operations. CEO Josh Whale explains:
"For a motorcycle driver with a petrol bike, the energy costs are around $2,000 a year. With us, that cost is reduced by about a third".
E-motos are also financially accessible, with a price tag of about $2,100 (including interest) and battery swaps costing approximately $1.60 (2,100 Rwandan francs) each. To make financing easier, the E-Moto Credit Enhancement Facility and rebate programs provide first-loss funding to banks and reduce down payment requirements for operators. By 2030, Rwanda aims to electrify 30% of its motorcycles, potentially saving the country $22 million annually in fuel import costs.
For businesses looking to make the switch, AUTO24.rw offers a range of electric motorcycles and commercial vehicles, making the transition to cleaner fleets more accessible than ever.
Monitor and Maintain Emission Reductions
Reducing emissions isn’t a one-and-done task – it’s an ongoing process that demands consistent tracking and maintenance to keep your fleet operating efficiently. Regular monitoring not only ensures compliance but also aligns with Rwanda’s broader efforts to minimize environmental impact.
Use Fleet Management Software
Fleet management software is a powerful tool for staying on top of vehicle performance and compliance. It simplifies meeting Rwanda’s mandatory emission testing requirements by automating tasks like inspection reminders through IremboGov, storing e-certificates digitally, and sending alerts for vehicles nearing non-compliance. These features help you avoid delays and take timely action. For additional guidance, resources such as the UNEP Clean Fleet Toolkit provide step-by-step strategies to reduce environmental impact. Plus, keeping records aligned with Rwanda’s Carbon Registry allows you to track and measure the progress of your emission reduction efforts.
Schedule Regular Maintenance
While digital tools are essential, mechanical upkeep is equally important for maintaining low emissions. Pairing mechanical inspections with emission tests through IremboGov ensures your fleet remains efficient and compliant. These services are available at Contrôle Technique centers in Remera, Rwamagana, Huye, and Musanze. Be sure to clear any outstanding traffic fines before booking inspections. If a vehicle fails an emission test, prioritize repairs and schedule a re-test quickly to avoid additional costs.
For businesses considering a switch to electric vehicles, there’s an added bonus: fully electric vehicles are currently exempt from mandatory emission inspections. Platforms like AUTO24.rw offer a variety of EV options, including Teslas, Leapmotor, and ROX, giving fleet operators an opportunity to simplify compliance while significantly reducing emissions.
Conclusion
Reducing fleet emissions in Rwanda not only improves operational efficiency but also plays a key role in achieving the country’s target of cutting carbon emissions by 38% by 2029. With road transport contributing 13% of Rwanda’s total greenhouse gas emissions, businesses have a clear opportunity to make a meaningful difference by adopting the right strategies.
Start by conducting a thorough audit of your fleet, optimizing routes to minimize idle time, and transitioning to electric vehicles – steps that can significantly lower fuel costs. Government incentives, including 0% VAT, import duty exemptions on EVs, and rent-free land for charging stations, make the financial case for this transition even stronger.
AUTO24.rw makes this shift easier with its selection of certified electric vehicles, ranging from Teslas to Leapmotor and ROX models, designed to meet the needs of delivery fleets and public transportation upgrades. This alignment of technology, policy, and business needs supports the strategies outlined earlier.
To maintain progress, implement fleet management software to monitor performance and ensure regular maintenance. By tracking your fleet’s impact against Rwanda’s 2030 goals, you can reduce emissions with every mile driven, contributing to cleaner air and a stronger, more sustainable economy. The tools and strategies are ready – it’s time to act.
FAQs
What are the benefits of switching to electric vehicles for fleet management in Rwanda?
Switching to electric vehicles (EVs) for fleet management can be a game-changer for businesses in Rwanda. By running on electricity rather than imported fuel, EVs help businesses cut fuel expenses and reduce reliance on fluctuating global oil markets. Plus, they come with lower maintenance costs since EVs typically require fewer repairs and less servicing compared to traditional vehicles with internal combustion engines. These savings add up, making EVs a smart choice for managing overall operational costs and freeing up resources for other priorities.
Beyond the financial perks, EVs play a key role in creating a cleaner and healthier environment. By cutting greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality – especially in bustling cities like Kigali – they directly support Rwanda’s climate initiatives. On top of that, adopting EVs can boost a company’s image, positioning it as a forward-thinking leader in sustainability. In an era where environmental responsibility matters more than ever, this can be a powerful way to stand out in the marketplace.
How can route optimization help reduce fleet emissions?
Route optimization plays a key role in lowering fleet emissions by cutting down the distance vehicles travel and minimizing unnecessary idling. GPS-based tools help map out the shortest or most efficient routes, which directly reduces fuel consumption. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, research indicates that trimming mileage by just 10% can result in a similar reduction in both fuel use and emissions, while also lowering vehicle wear and maintenance expenses.
In Rwanda, smarter routing offers even more benefits. Besides cutting emissions, it helps ease traffic congestion, particularly on heavily traveled roads. Vehicles spend less time stuck in stop-and-go conditions, which are notorious for wasting fuel. By tapping into real-time traffic data and streamlining deliveries, businesses can boost vehicle efficiency, save on fuel costs, and promote cleaner air in urban areas – all while shrinking their carbon footprint.
What benefits are available for businesses switching to electric buses and motorcycles in Rwanda?
Rwanda has introduced a range of incentives to make it easier and more affordable for businesses to switch to electric buses and motorcycles. These include tax exemptions on import duties, excise taxes, and VAT for fully electric vehicles. On top of that, registration fees are reduced, cutting down the overall cost of owning an electric vehicle.
For fleet operators, the government offers low-interest loans and grants through climate-resilient transport initiatives to help with the purchase of electric vehicles. There’s also financial support for converting gas-powered motorcycles to electric, with subsidies covering part of the conversion costs. To ensure a smooth transition, training programs are available for technicians working on these conversions.
Companies adopting electric buses can benefit from funding for charging infrastructure, faster customs procedures, and even priority consideration in public-sector procurement. These measures are designed to encourage businesses in Rwanda to embrace electric fleets while keeping costs manageable.
Related Blog Posts
- Carbon Offsetting in Rwanda: How It Works
- Rwanda’s ICE Vehicles: Carbon Emissions Impact
- Rwanda’s Plan for 20% Electric Buses by 2030
- Electric vs Petrol cars in Rwanda





