Rwanda is making strides toward integrating electric vehicles (EVs) into its transportation system, aiming to cut greenhouse gas emissions by 38% by 2030 and achieve a carbon-neutral economy by 2050. With clear targets and supportive policies, the country has already seen growth in EV adoption. However, challenges like high costs, limited charging infrastructure, and rural accessibility remain.
Key Takeaways:
- Government Policies: Tax exemptions on EVs, reduced corporate tax rates, and rent-free land for charging stations are driving adoption.
- Infrastructure Growth: 24 public charging stations and 49 battery-swapping stations exist, but rural areas need more coverage.
- Adoption Rates: EVs increased from 19 in 2020 to 512 by 2024, with 4,000+ electric motorcycles already in use.
- Challenges: EV prices remain high, rural areas lack infrastructure, and only 53% of the population has electricity access.
Rwanda has laid a solid foundation with clean energy resources and forward-thinking policies but needs to address affordability and infrastructure gaps to ensure widespread EV adoption.
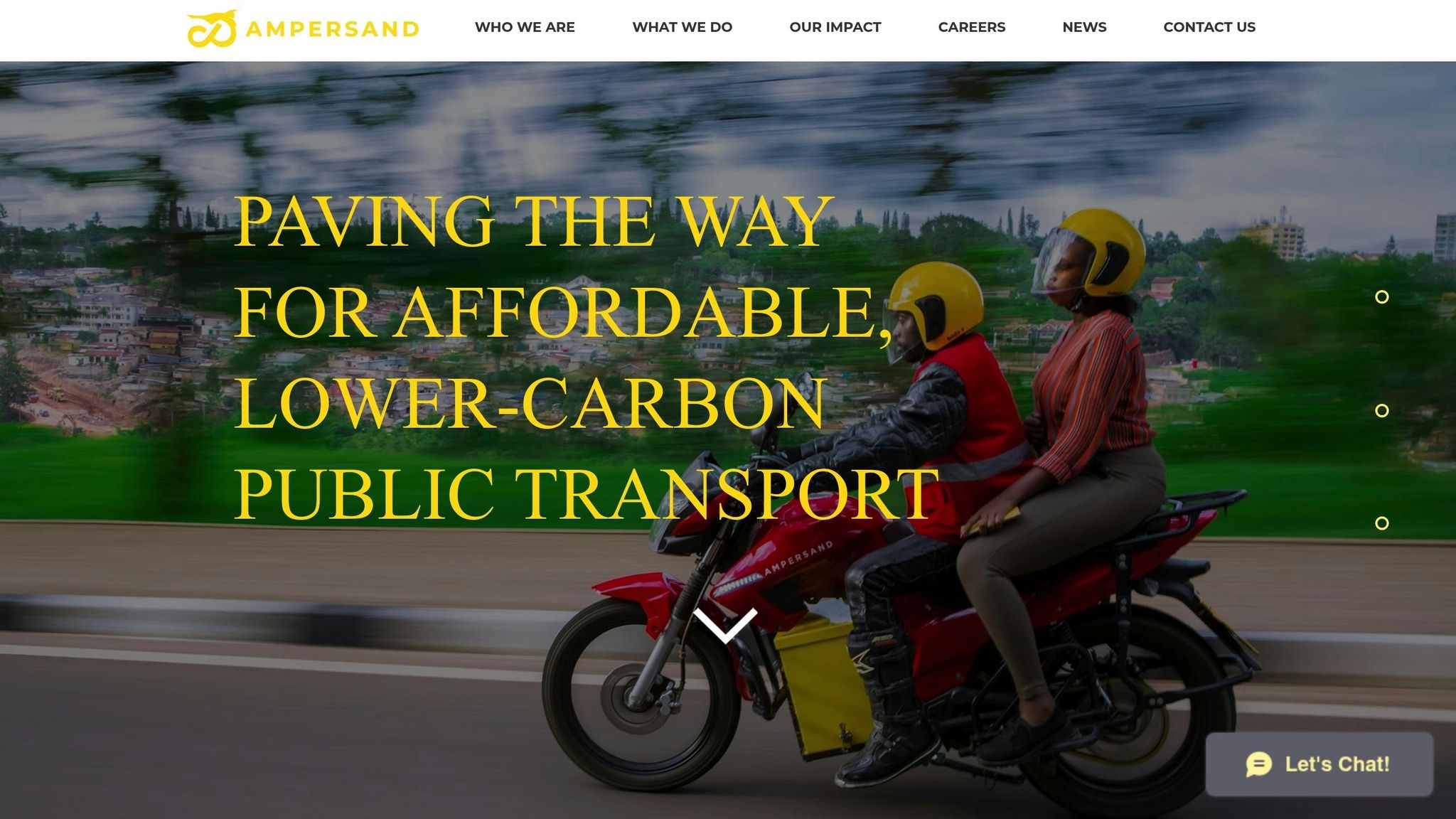
Ampersand‘s 1000 E-motorcycles on East African Roads
1. Government Policies and Incentives
Rwanda has implemented a range of financial incentives aimed at accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) nationwide. These policies are designed to support various aspects of the EV ecosystem, from manufacturing to the development of charging infrastructure.
One of the cornerstones of Rwanda’s EV strategy is tax exemptions. Electric vehicles, along with their spare parts, batteries, and charging station equipment, are fully exempt from import and excise duties. Additionally, they benefit from a zero-rated Value Added Tax (VAT). This approach not only makes EVs more affordable but also supports the entire supply chain critical to their operation.
"The Government decided to extend incentives on Electric & Hybrid vehicles and Electric motorcycles to pay an import duty rate of zero. This intends to accelerate the transition to Electric Vehicles and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from vehicle transportation. It is reviewed on an annual basis", states Rwanda’s Ministry of Finance.
To attract EV manufacturers and assembly operations, the government offers preferential corporate tax rates. Companies that set up manufacturing or assembly facilities in Rwanda can take advantage of a reduced corporate income tax rate of 15%, along with tax holidays. This significant reduction from standard tax rates positions Rwanda as an appealing destination for international EV companies.
The government has also removed barriers for expanding the charging network. Operators of charging stations are granted government land rent-free, and electricity for charging is billed at industrial tariffs to ensure competitive pricing. These measures aim to make charging infrastructure more accessible and affordable.
Commercial vehicle electrification is a particular focus of Rwanda’s policies. DG Byiringiro, Director General for Transport, highlights the broader goal behind these incentives:
"The incentives will also play a role to mobilize investment into the e-mobility sector which has fast emerged as a top sector on demand".
Rwanda regularly reviews its EV policies to adapt to changing market conditions. For example, while the government continues to strongly support fully electric vehicles, it has started reconsidering incentives for hybrid vehicles to encourage a shift toward cleaner technologies. Between 2020 and 2024, Rwanda imported 7,172 hybrid and electric vehicles, but only 512 (7%) of these were fully electric. This data has driven recent policy changes aimed at prioritizing fully electric vehicles over hybrids.
In addition to these incentives, Rwanda collaborates with international organizations like the Global Green Growth Institute, United Nations Environment Programme, International Finance Corporation, and the World Bank. These partnerships help create a supportive environment for sustainable mobility.
2. EV Charging Infrastructure and Market Accessibility
Rwanda’s EV charging network is growing, but there’s still a noticeable gap between urban hubs and rural areas. As of August 2024, the country has 24 public charging stations, 4 direct chargers for motorcycles, and 49 battery-swapping stations. While this setup meets the needs of Kigali and its surroundings, it highlights the challenges faced by potential EV owners in more remote regions.
In Kigali, charging stations are strategically located along major roads, in shopping centers, and within business districts. However, the real challenge lies in extending this convenience to the entire country. To address this, the government is working on an ambitious plan to ensure no vehicle travels more than 31 miles (50 kilometers) without encountering a charging station. A geospatial analysis has already identified over 224 potential sites for new EV charging stations across Rwanda.
One major hurdle is electricity availability. Rwanda currently has 225 MW of installed electricity capacity, with just 53% of the population connected to the grid. Expanding EV infrastructure in rural areas with limited electricity access will require careful planning and innovative solutions.
"People want to buy EVs, but they don’t have the confidence when they consider the limited charging stations available, and especially if they want to travel upcountry, it becomes even more difficult." – Srinivas Cheruvu, Managing Director of CFAO Mobility Rwanda
To address gaps in fixed charging infrastructure, mobile and on-demand charging services are being introduced. Additionally, Rwanda is tapping into its renewable energy resources – over 50% of its electricity is generated from hydroelectric and solar power. For instance, Kabisa launched EV House in Kigali in April 2025, featuring solar panels installed by Meshpower for off-grid charging. The company also introduced an ultra-fast charging station at SP’s Kanombe location, offering chargers with up to 240 kW capacity that can fully charge vehicles in 15–25 minutes.
"We’re truly only getting started." – Pophia Muhoza, Kabisa Rwanda Managing Director
Despite infrastructure challenges, the market is showing signs of progress. The number of electric vehicles in Rwanda grew from just 19 in 2020 to 512 in 2024, while hybrid vehicles reached 6,660. Kabisa plans to establish 38 EV charging stations by the end of 2024, ensuring a station approximately every 62 miles (100 kilometers). Ampersand, another key player, operates 32 battery-swapping stations in Kigali and aims to manufacture 18,000 batteries by 2025.
For EV owners, practical tips like carrying charging adapters and basic toolkits are essential when traveling outside Kigali. The government also encourages charging during off-peak hours to ease pressure on the grid. These measures highlight that while the infrastructure is improving, thoughtful planning is still necessary for EV users.
Efforts to expand the network are extending to cities like Musanze, Huye, and Rubavu. Additionally, eco-tourism is playing a role in this growth, with eco-lodges installing EV chargers to attract environmentally conscious travelers.
Pros and Cons
Rwanda’s journey toward electrifying its transportation sector reveals a mix of opportunities and hurdles, shaped by the country’s policies and infrastructure developments. Here’s a closer look at the current landscape:
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| – Ambitious Government Goals: The government has set clear electrification targets, supported by robust policies. – Clean Energy Backbone: Rwanda’s reliance on renewable energy strengthens the environmental benefits of EVs. – Environmental Benefits: With road transport contributing 13% of the nation’s greenhouse gas emissions, EVs play a key role in reducing carbon output. | – High Costs: Electric vehicles are still far more expensive than traditional cars, making them less accessible for most Rwandans. – Limited Charging Infrastructure: The existing network is insufficient for the growing demand. – Rural Challenges: Charging stations are scarce in remote areas, creating an urban–rural divide. – Skill Gaps: A shortage of technical expertise could hinder maintenance and service capabilities. – Small Market: The limited size of Rwanda’s market makes it less attractive for private sector investment in EVs. |
Transitioning to e-mobility in Rwanda comes with a hefty price tag – an estimated $900 million. Despite this, the government remains committed to the cause. François Zirikana, an e-mobility expert from the City of Kigali, emphasized:
"E-mobility is one of the transport decarbonization initiatives the government has undertaken".
However, the challenges aren’t evenly distributed. Kigali, the capital, enjoys relatively better charging infrastructure, but extending these networks to rural areas – where even basic electricity access can be limited – poses significant financial and logistical obstacles. This disparity risks concentrating EV adoption in urban centers, leaving rural regions behind.
While Rwanda’s renewable energy resources provide a strong foundation for the EV transition, addressing the issues of affordability, infrastructure, and expertise is essential for achieving widespread adoption. Without resolving these gaps, the benefits of e-mobility may remain out of reach for much of the population.
sbb-itb-7bc66b5
Conclusion
Rwanda is at a key turning point in its journey toward embracing electric vehicles (EVs). The groundwork has been laid with progressive government policies, expanding renewable energy systems, and growing interest among consumers. For instance, recent data highlights a notable increase in the import of hybrids and electric motorbikes, signaling a shift toward greener transportation options.
That said, infrastructure gaps remain a pressing concern. The lack of widespread charging stations, especially in rural areas, continues to hinder confidence in EV adoption for long-distance travel. To address this, the government’s initiative to ensure no EV is more than 31 miles (approximately 50 kilometers) away from a charging station is a step in the right direction.
Financial challenges also persist, but the government has introduced measures like tax exemptions and affordable electricity rates – set at $0.10/kWh with 82% access expected by 2024 – to ease the transition.
To accelerate progress, Rwanda can focus on three critical areas: building more rural charging stations through public-private partnerships, introducing EV education programs to boost consumer trust, and investing in technical training to nurture local expertise. These steps would ensure a more inclusive and sustainable EV ecosystem.
International collaborations are also playing a pivotal role. The recent introduction of the Article 6 Carbon Market Framework project, backed by $854,859 in funding, underscores how global partnerships can drive local advancements.
With its clean energy mix – including geothermal and methane resources – Rwanda stands out as a leader among African nations in renewable energy. These efforts align seamlessly with the country’s 2050 carbon-neutral goal, showcasing a strong commitment to sustainable transportation. While challenges like affordability and infrastructure expansion remain, Rwanda’s vision is clear. By maintaining consistent policy support and prioritizing strategic investments in charging networks, the country is well-positioned to lead the region in sustainable mobility.
The task ahead is to scale infrastructure to match its ambitious vision and the growing demand for EVs. Rwanda’s progress so far suggests it’s ready to meet this challenge head-on.
FAQs
What is the Rwandan government doing to expand EV infrastructure in rural areas?
The Rwandan government is making strides to expand electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure in rural areas by setting up 36 charging stations and developing a master plan to keep charging points within 30 miles of each other. To support this, they’re offering land for charging sites and incorporating EV infrastructure requirements into building codes.
These steps are part of a larger effort to make EV adoption easier nationwide, particularly in less urbanized areas. By tackling infrastructure challenges and encouraging sustainable transportation, Rwanda is carving out a prominent role in advancing green mobility across Africa.
What is Rwanda doing to make electric vehicles more affordable for its citizens?
Rwanda’s Push for Affordable Electric Vehicles
Rwanda is making bold moves to bring down the cost of electric vehicles (EVs) and make them more attainable for its citizens. One of the standout initiatives is the removal of VAT on EV imports, along with exemptions on import and excise duties for EV parts. These financial breaks are designed to cut the upfront costs, making EVs a more realistic option for buyers.
The government isn’t stopping there. To encourage investment in the EV sector, businesses can benefit from a reduced corporate income tax rate of 15%. On top of that, Rwanda is working to expand its charging network by offering land grants for charging station projects and supporting ventures like the Kabisa EV House in Kigali. Through these combined efforts, the country aims to build a more accessible and greener e-mobility system for everyone.
How are international partnerships helping Rwanda adopt electric vehicles?
International Partnerships and Rwanda’s EV Transition
International collaborations are proving to be a game-changer for Rwanda as it moves toward adopting electric vehicles (EVs). By teaming up with global companies, Rwanda gains access to cutting-edge technology, financial resources, and specialized expertise. These partnerships are fueling local production efforts, such as manufacturing electric motorcycles, which are laying the groundwork for a thriving EV market and the necessary infrastructure to support it.
Organizations like the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) are stepping in to support Rwanda in its fight against air pollution. UNEP’s involvement extends to helping shape policies that encourage the adoption of EVs, creating a more eco-friendly transportation landscape. These collaborations are not just about technology – they’re about sharing knowledge, driving innovation, and speeding up Rwanda’s journey toward cleaner, greener transportation options.
Related posts
- EVs vs. ICE Cars: Performance on Rwanda’s Roads
- Rwanda’s ICE Vehicles: Carbon Emissions Impact
- Rwanda’s Plan for 20% Electric Buses by 2030
- Electric vs Petrol cars in Rwanda





